SEO Trends in 2020: What’s Changed and What’s Coming
24 December 2020 Leave a comment ALL-HANDS SEO
2020 has been a tough year. The COVID-19 pandemic, bushfires in Australia, stock market crash, Iranian missile strike — you name it. It’s hard even to recall all this year’s main turmoils because there were too many of them. No doubt, a lot has happened, and the world as we knew it has completely changed.
So has SEO.
This year has also been rich in SEO-related events. It has almost come to its end, and we think it’s just the time to discuss what optimization trends were shaped in 2020 and what to expect from the upcoming year.
SEO trends 2020: what has changed
We believe the most notable changes in SEO were the following:
- Google updated its Search Console several times. While most of the updates were handy and useful, there is one update that disappointed many SEO experts.
- Google rolled out three core updates. Even though core updates aren’t supposed to target any specific categories, these ones have broken the rule.
- Google started doing its best to support businesses during the COVID-19 pandemic. It implemented many new features and made both business owners’ and their customers’ lives much more comfortable.
Want to know more? Keep reading — we’re about to get all these events in the raw one by one.
Google Search Console: give with one hand, take away with the other
Google constantly updates its Search Console to make it more convenient for users. However, sometimes the search engine removes something webmasters find useful. That’s exactly what happened in 2020. Even though Google added new features and improved some old ones, it also made changes that were rather frustrating to the SEO community.
News search type filter
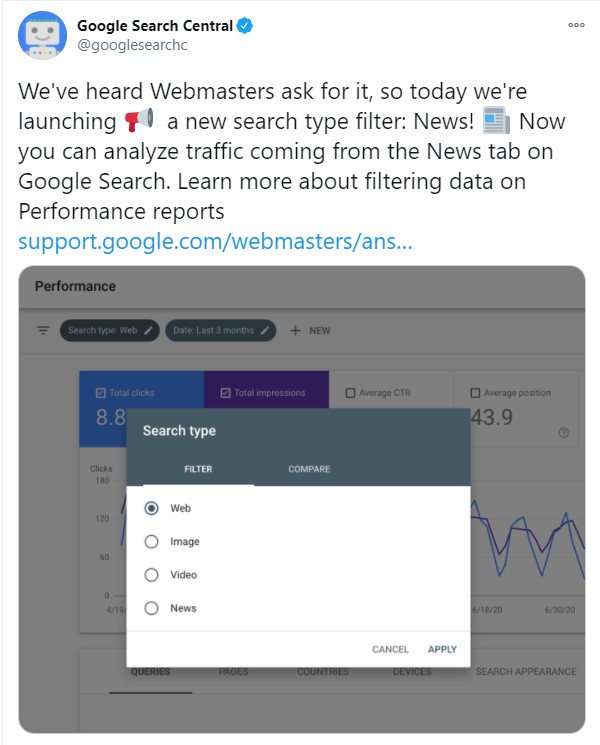
Google claims it sends people to news websites over 24 billion times a month. Up until now, you couldn’t analyze how much traffic came to your site from the News tab.
On July 21, Google launched a new search type filter called News.
It can be accessed from the Performance report. You can apply it to discover how many users visit your website from the News tab alone and analyze that data for your own purposes.
That is definitely one handy feature, isn’t it? We could have been rejoicing about it all year long, but there is one little fly in the ointment that spoiled our joy.
Request indexing feature removal
Not all Search Console updates make the tool convenient. Some do exactly the opposite.
As you probably know, you could manually request Google to index your website’s pages with the request indexing feature before. It was extremely handy as it made the indexation process much faster.
However, on October 14, Google removed that feature from Search Console to make some infrastructure changes.
Google representatives stated that it was a matter of a few weeks for the feature to return, but it’s December already, and it’s still disabled.
We don’t know whether this feature is coming back or not. However, Google’s John Mueller hinted that it might be available again.
A user asked him:
“What’s up with the request indexing thing? …Are you taking it away from us?”
And John’s reply was:
“I’m not planning on taking away anything.”
Also, in the latest Q&A, he told Search Engine Land that he was personally pushing the Search Console team to find a solution to this problem.
So all we can do is wait and see. Meanwhile, let’s discuss something more uplifting.
Better data export, new Removals Report, and improved crawl stats
In addition to implementing the News search filter, the Search Console team also improved data export, the Removals report, and crawl stats:
- Better data export. Now users can export chart data in addition to tables.
- New Removals report. Search Console’s removals tool enables webmasters to hide their websites’ specific pages from search results. An updated Removals report can now tell users which of their URLs were refined by Google SafeSearch’s adult filter and which content was labeled as outdated.
- Improved crawl stats. A new version of the crawl stats report helps webmasters better understand how Googlebot crawls their websites. Now it has some new features and provides more detailed information. You can learn more about it in this Google Search Central blog post.
These were all the most significant updates in Google Search Console for 2020. Now it’s time to discuss something even more important, something that affects millions of websites globally. We are talking about Google core updates.
Google Core Updates: your money or your life?
Google constantly tweaks its search algorithm. While the vast majority of updates are small and relate to specific niches, there are also major ones that affect most websites globally. They’re called core updates.
In 2020, Google rolled out three core updates:
- the January 2020 core update;
- the May 2020 core update;
- the December 2020 core update.
Even though Google states that core updates don’t target specific categories, many SEO experts have noticed significant ranking shifts in the YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) category. It includes travel, retail, finance, health, sports & news, and arts & entertainment niches.
Let’s begin with the January 2020 core update.
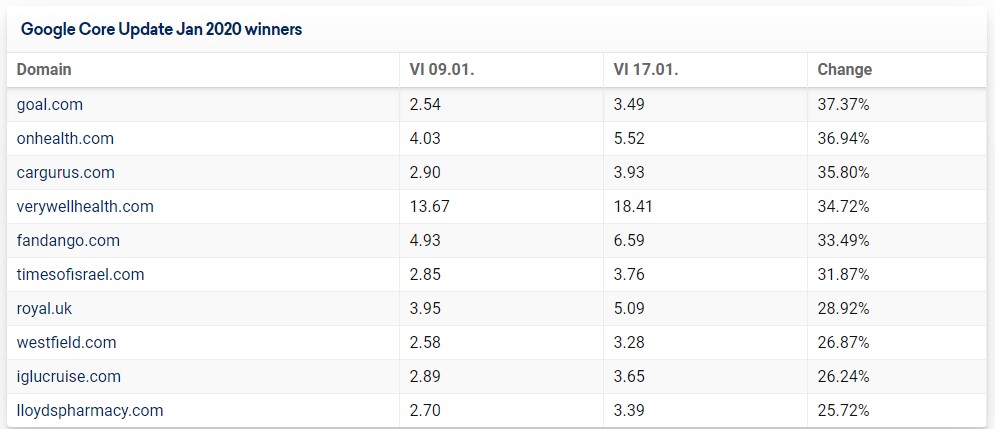
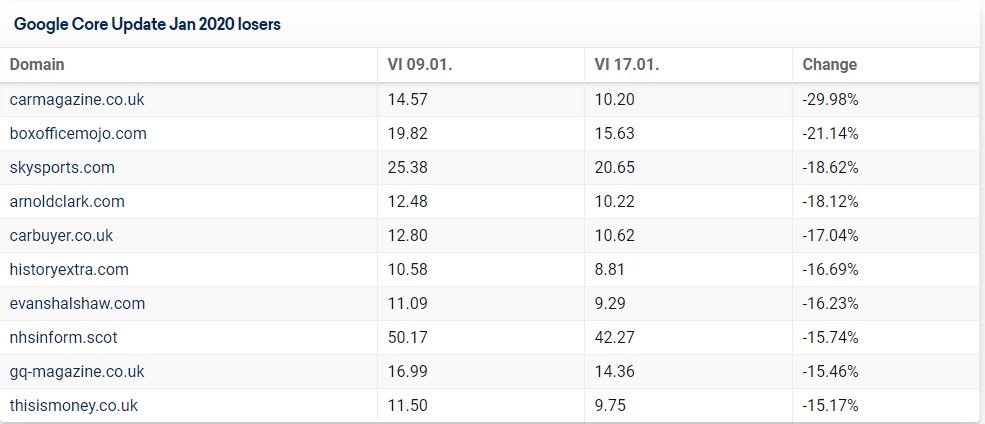
Sistrix’s revealed the winners and losers of this update.
Here are the winners:
And here are the losers:
According to Sistrix, YMYL websites were re-evaluated by search algorithms and gained or lost visibility as a whole. They believe domains that had been previously affected by such updates were affected again.
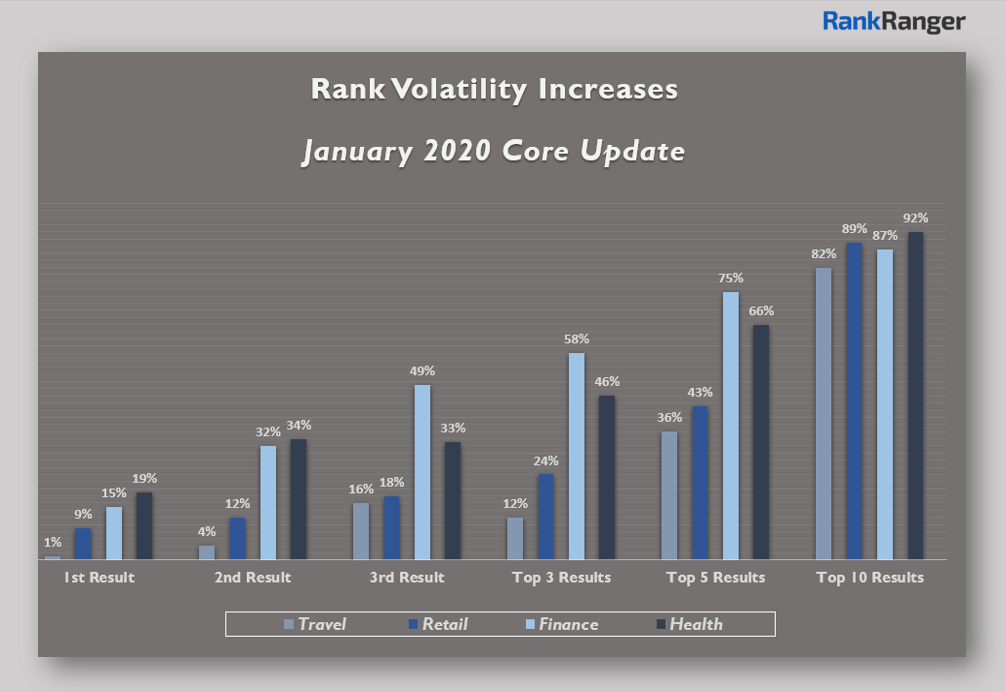
Rankranger also did research and discovered that the overall rank volatility was extremely high at the TOP10 results of SERP.
According to them, the ranking shifts were the most noticeable in health and finance niches, both of which are in the YMYL category.
But maybe the case with the May 2020 core update was different?
Many SEO experts believe it was about E-A-T (Expertise, Authority, Trust). And there is one study that proves this point.
The MHC team analyzed hundreds of websites of their clients and concluded that the following changes were part of the May 2020 core update:
- Google started understanding users’ intent better and providing more relevant search results.
- The search engine emphasized expertise. Many articles that won their rankings contained an element of first-hand expertise.
- Even though Google continued focusing on authority, some less authoritative websites managed to outrank the most authoritative ones.
- Google reassessed signals that help it determine website E-A-T.
- The search giant punished websites that had unnatural backlinks.
But! If we look at the winners and losers of this update, we’ll discover that the YMYL category was the most volatile once again.
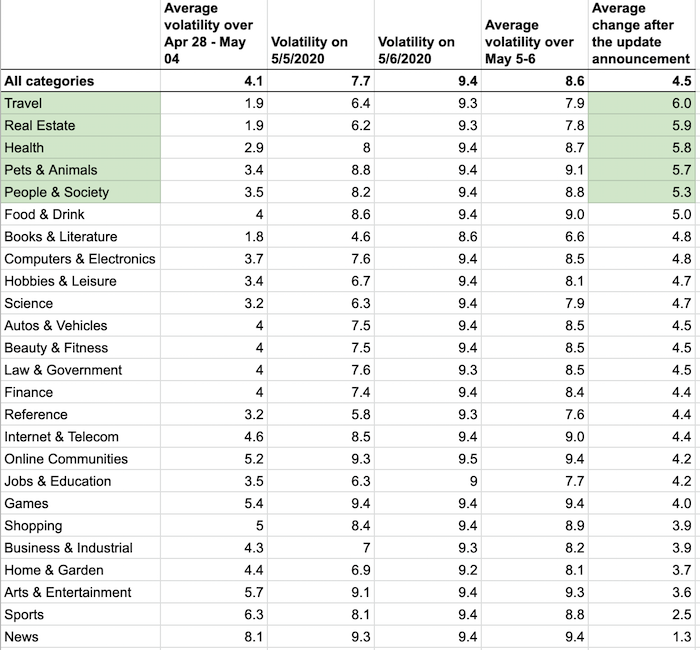
Let’s just look at the analysis by SEMRush.
As you can see, travel, real estate, health, pets & animals, and people & society niches experienced the biggest ranking fluctuations. That means the May 2020 core update has also affected the YMYL category just like the previous one.
But what if the December 2020 core update was different?
Google rolled it out just a few days ago, so it’s too early to analyze the update’s full impact on SEO. However, some experts have already witnessed considerably high levels of volatility in the YMYL category.
According to Glenn Gabe of GSQi, the YMYL content is held to a higher standard. He believes webmasters should be careful when mixing commerce or affiliate marketing with health and medicine as there’s a fine line between educating and selling. He saw several websites that did it wrong and eventually got punished by the December 2020 core update.
That proves that this core update has also affected the YMYL category, just like all previous core updates in 2020.
It’s not far-fetched to suggest that future core updates will affect the YMYL category as well, so if your website’s in it, you should choose your optimization strategies wisely.
But let’s not think ahead. It’s better to talk about something that has happened already: for example, about new pandemic-related features implemented by Google.
Pandemic-related features: Google is doing its best to support businesses
The COVID-19 pandemic has completely changed the way many businesses operate. Google understands that, so it continually creates new features to help companies during this challenging period. In 2020, the search giant did many useful updates.
Schema markups for special announcements
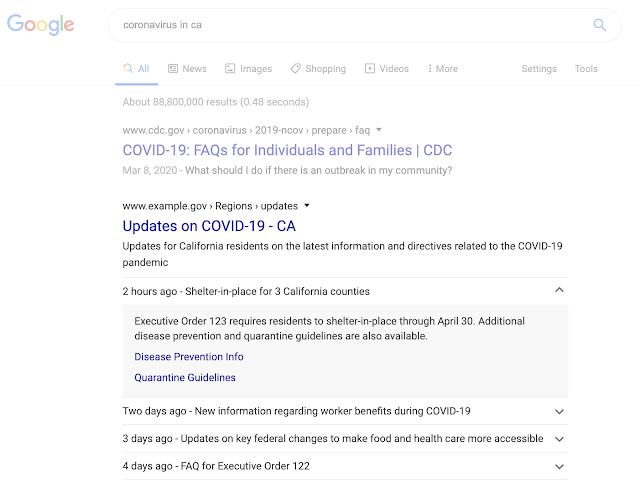
During the COVID-19, many businesses are closing, changing their work hours, or rescheduling some events. To help them inform their customers about such changes, Google introduced a way to highlight COVID-19 announcements on Google Search.
Business owners can now add Special Announcement structured data to website pages so that their content appears with a COVID-19 announcement rich result.
That way, people who search for their companies on Google will stay notified about any important events related to the pandemic.
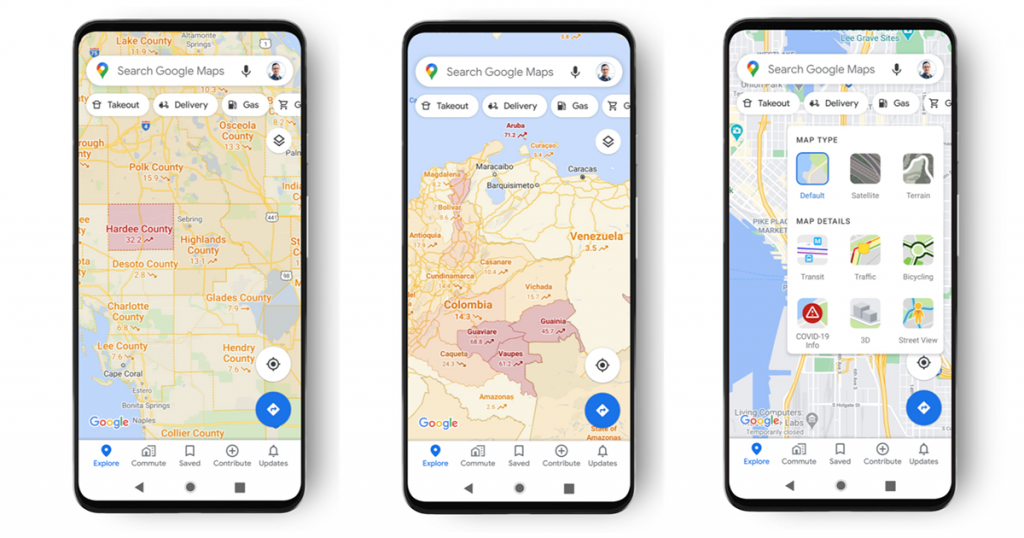
COVID-19 Google Maps updates
Google Maps has also adapted to the COVID-19 outbreak. Now people can:
- search for health facilities that support testing for coronavirus;
- enable an overlay of COVID-19 case trends on mobile devices;
- make business-related updates;
- get in-app alerts if their routes are affected by pandemic-related restrictions;
- find restaurants that offer take-out and delivery.
These updates are pretty handy as they enable users to get information about a specific place without having to visit it.
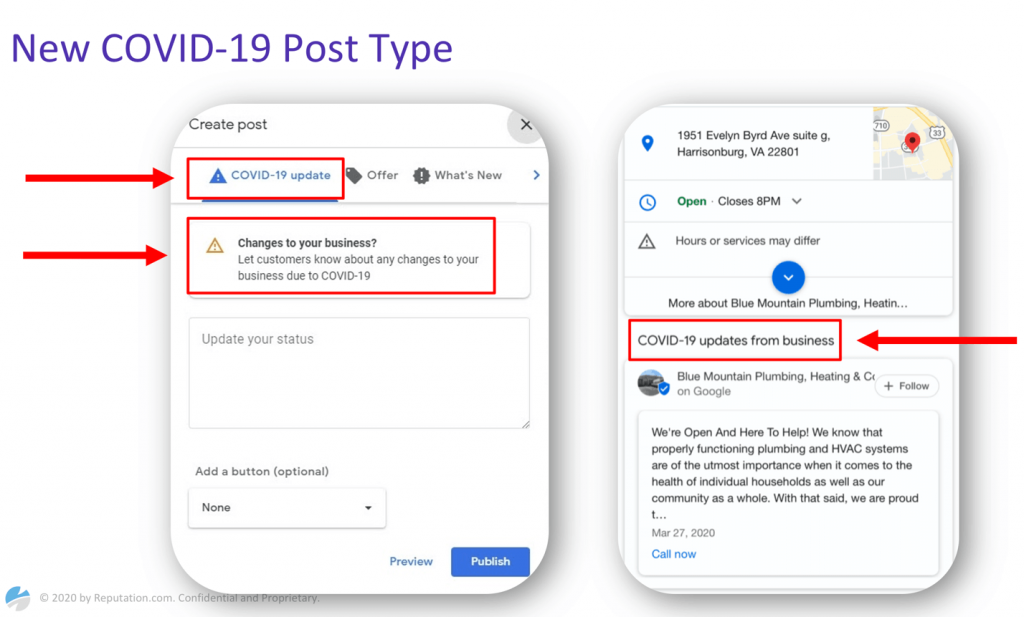
New Google My Business features
Google also made several updates to Google My Business. Now businesses can create COVID-19 type posts. Such posts are labeled as pandemic-related information and always appear above regular posts.
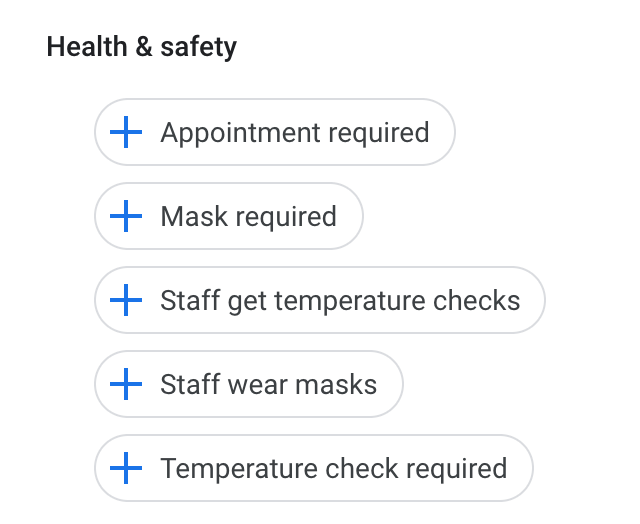
Also, Google launched Health & Safety attributes. It enabled food, retail, and service businesses to add these attributes to inform customers about several safety measures in their places.
In addition to the above, Google allowed businesses to set special hours. They can schedule them for holidays, special events, or other exceptional circumstances. That way, their customers will be able to know at a glance when to go to a particular place and for what purpose.
And that’s not all. Google also enabled businesses to create support links so that users can make donations to them or purchase their gift cards. However, starting this December, companies can’t create new support links anymore, but they can still create posts in the Updates tab with links to donation campaigns or gift cards.
Now that we described the most notable SEO changes in 2020, it’s time to discuss what the upcoming year may bring us.
What SEO will be like in 2021
Even though Google often acts like an unpredictable woman and rolls out its updates with no warning, sometimes it notifies webmasters about future changes beforehand. Thus, we can be sure that in 2021 Google will emphasize user experience on mobile devices. It’s confirmed that:
- Google will switch to mobile-first indexing in March 2021;
- the search engine will start measuring several mobile UX metrics and using them as ranking signals.
And what we personally believe is that Google will continue turning itself into an answer engine.
Now let’s discuss all of this in more detail.
Google will have switched to mobile-first indexing by March 2021
Smartphones are taking over the world. In 2019, 63% of all website traffic in the US came from mobile devices. There are approximately 3.5 billion smartphone users worldwide, so it’s no wonder mobile-first indexing has been one of ongoing Google’s efforts for several years.
The search engine planned to enable mobile-first indexing in September 2020 but eventually extended the timeframe to March 2021. That means by that date, your website’s mobile version will have been the starting point for the Google index.
It doesn’t mean Google will stop indexing desktop versions of websites, though. After enabling the mobile-first indexing, the search engine will still occasionally crawl the desktop versions of sites, but most crawling will be done with Google’s mobile user-agent.
So if you want to rank well in 2021, you have to start preparing for this update. You have to make sure that:
- your website has a responsive design appropriate for smaller screens,
- its pages load fast enough on mobile devices;
- the site doesn’t have annoying pop-ups that are impossible to close on smaller screens;
- your content is mobile-friendly: it has readable fonts and proper text formatting;
- your website is easy to navigate on mobile devices.
By making a website mobile-friendly, you will eventually improve its rankings even for the desktop. So why not optimize it? Actually, we have one tool that can help you with it. It’s called Lighthouse.
This tool will analyze your website, show its performance for mobile and desktop devices, and provide you with useful tips on improving it. It will help you optimize for mobile-first indexing and get prepared for mobile-related updates in 2021. Yes, you read it correctly. We wrote updates because there is one more update coming that is related to user experience on mobile devices.
Core Web Vitals: user experience on mobile will be a ranking factor
We already mentioned this in our recent blog post about upcoming SEO trends. But repetition is the mother of learning, so let’s discuss it once again.
At the end of May 2020, Google announced that it would roll out an update focused on mobile user experience on a particular page. The update will combine the Core Web Vitals metrics with Google’s existing signals to determine the quality of UX a certain page provides and rank this page accordingly.
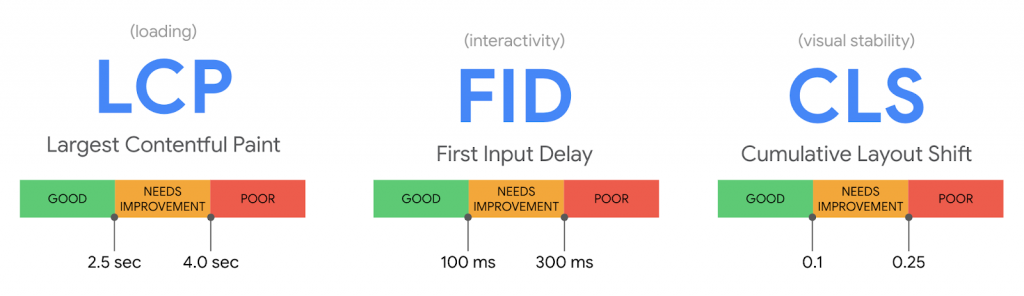
Google will start measuring:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP);
- First Input Delay (FID);
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS).
To avoid duplicate content issues, we won’t describe each of these metrics once again. If you want to learn more about them, just read our article on SEO trends. In short, LCP measures a page’s load speed, FID — its responsiveness, and CLS — the visual stability of its layout.
As we just said, Google will soon start measuring these metrics to determine website rankings, so it’s better to prepare for it. Even though the Core Web Vitals update isn’t rolled out yet, you can already track each of these metrics with the Web Vitals extension for Chrome. Just download it for free from the Chrome web store.
If you don’t want to install any software, you can use our Lighthouse tool. It also can display all Core Web Vitals metrics.
That way, you will find the weak parts of your website and will be able to improve them ahead of the future update.
Google will continue answering user queries in SERP
Let’s be honest: Google doesn’t care about your website’s traffic — it cares about satisfying its users.
Google has been working hard to provide answers to users’ questions right in SERP. It’s created answer boxes, knowledge graphs, featured snippets, carousels, and other extra SERP elements so that people can find what they are looking for without visiting any website.
Even though SERP features steal our traffic, we have to admit they are extremely convenient for internet users. Moreover, some of the SERP features are clickable, so they can bring traffic to your website if you manage to get your content featured in them. So why not try to optimize for them? Maybe some of the future snippets will be clickable as well, so it’s a good idea to prepare your content beforehand.
How to optimize your website for SERP features
There are a few things you can do to try to show up in SERP elements:
- answer users’ questions briefly;
- find related questions for your topic and answer them to have a chance to show up in the people also ask section;
- create a Google My Business account so that your company info can appear in the knowledge graph;
- always specify titles and alt tags of the images you use to show up in the “Images” section;
- use Schema markup to optimize for rich snippets and run Google rich results test to make sure you did everything right;
- embed a video to your website so that it can appear in the Videos section.
Also, grab your free copy of our guide to winning quick answers. It explains what zero position is, how it can help your business, and what is needed to get your website into this sweet spot.
Conclusion
Just like 2020, this blog post turned out to be longer than we anticipated. We hope you made it to the end and enjoyed reading it as much as we enjoyed writing it.
We know that a small percentage of people prefer to read conclusions instead of whole articles. That’s why we will sum up everything that was mentioned above.
Let’s start with what has changed:
- Google made several Search Console updates. It created a new search type filter that enables you to isolate and analyze traffic coming from the News tab. Also, Google improved crawl stats, data export, and the Removals report. However, it removed the request indexing feature that many webmasters used a lot.
- Google rolled out three core updates. SEO experts analyzed them and discovered that the YMYL category experienced the most ranking fluctuations.
- Google created several pandemic-related features. It made Schema markups for special announcements, updated Google Maps, and implemented new Google My Business features.
Now let’s describe what awaits us in 2021:
- Google is planning to enable mobile first-indexing in March 2021. That means your website’s version for mobile will be indexed prior to the desktop version.
- Google will be using Core Web Vitals metrics to rank websites. These metrics will help the search engine determine whether your site provides a good user experience on mobile devices or not.
- Google will continue turning into an answer engine. That means that we will probably see new SERP features in 2021.
So get ready for future updates before they affect your website in a bad way. Start doing it with RankActive tools — they will make your SEO routine much faster, easier, and productive.
Tags: Lighthouse, SEO trends, seo trends 2020, seo trends 2021, website audit, What will SEO be like in 2021, what's coming in SEO
Like this article? There’s more where that came from.
- 5 Questions to Ask Yourself Before Paying for Rank Tracking Software
- 5 Serious Mistakes Beginner SEOs Make and How to Fix Them
- Why We Use Google’s New Link Attributes and You Should Too
- Title and Description in 2021: Why Google Rewrites SEOs’ Meta Tags
- What We Should Learn From Google’s “About This Result” Feature